Ford Coyote V8: Oil Consumption Monitoring Guide
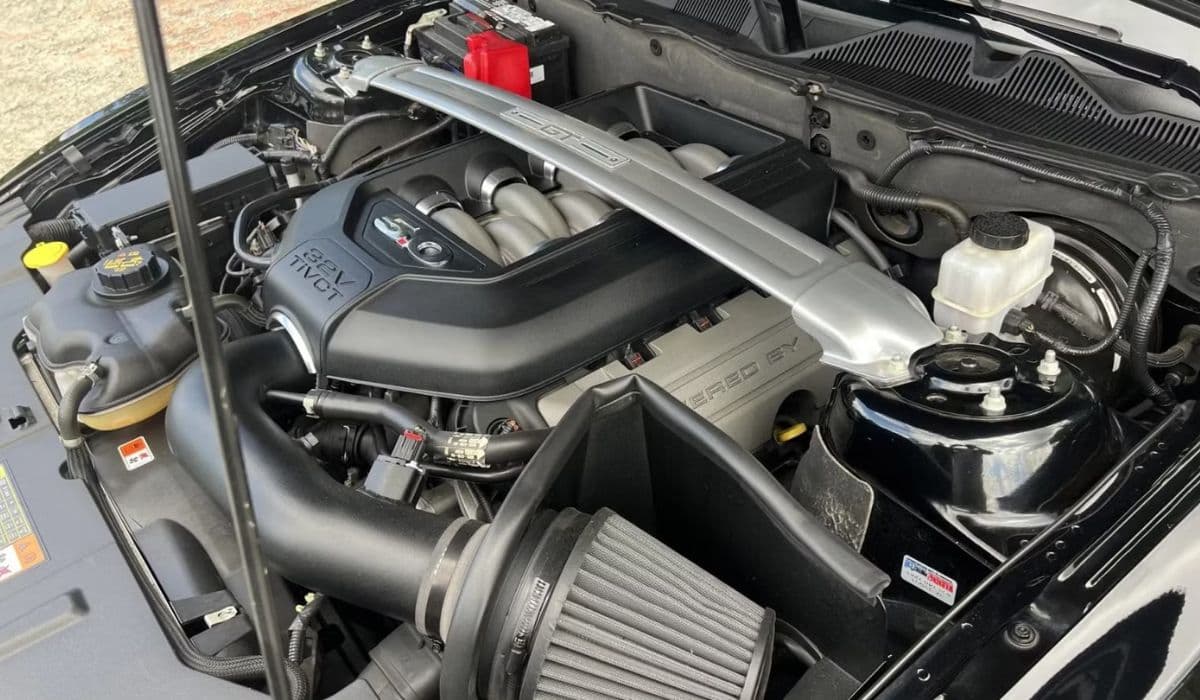

The Ford Coyote V8 stands as a pinnacle of modern American muscle, powering icons like the Mustang GT and F-150 trucks since its debut in 2011. This 5.0-liter naturally aspirated powerhouse delivers thrilling performance with up to 500 horsepower in various iterations, blending advanced technologies such as dual overhead cams, variable valve timing, and high-flow cylinder heads. Yet, beneath its roaring capabilities lies a critical aspect every owner must grasp: oil consumption. This isn't just about topping off fluids; it's about preserving the engine's longevity and efficiency. Early generations, particularly from 2011 to 2014, faced scrutiny for higher-than-average oil use due to piston ring designs and valve stem seals, while later models refined these elements for better control.
What makes the Coyote unique is its high-revving nature, often pushing boundaries in spirited driving or towing scenarios. Oil serves as the lifeblood, lubricating moving parts, cooling components, and sealing combustion chambers. Excessive consumption can signal underlying issues, from minor leaks to severe wear, potentially leading to costly repairs if ignored. By mastering monitoring techniques, enthusiasts can turn potential problems into proactive maintenance, ensuring their Coyote hums smoothly for years.
Why Oil Consumption Matters in High-Performance Engines
In high-performance setups like the Coyote V8, oil consumption isn't inherently bad—it's a natural byproduct of intense operation. Engines under heavy load generate more heat and pressure, causing small amounts of oil to burn off or evaporate. However, when rates exceed manufacturer norms (typically around one quart every 3,000 miles), it warrants attention. Ignoring this can lead to low oil pressure, increased friction, and eventual engine knock or failure.
Factors influencing consumption include driving habits, such as frequent high-RPM shifts or track days, which accelerate oil breakdown. Environmental conditions play a role too; hot climates or dusty roads can exacerbate evaporation and contamination. For Coyote owners, staying vigilant means avoiding surprises like blue exhaust smoke or fouled spark plugs, which are telltale signs of trouble brewing inside the block.
Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Oil Levels
Monitoring oil in your Coyote V8 starts with routine checks, ideally every 500 to 1,000 miles or before long trips. Begin by parking on a level surface and allowing the engine to cool for at least 30 minutes to ensure accurate readings—hot oil expands and can mislead measurements.
Locate the dipstick, usually marked with a yellow handle near the passenger side of the engine bay.
Pull it out, wipe it clean with a lint-free cloth, then reinsert it fully before pulling again to read the level.
Check against the hash marks: the oil should sit between the low and full indicators. If low, add the recommended 5W-20 or 5W-30 synthetic blend gradually, rechecking after each addition.
Note the color and consistency—milky oil might indicate coolant contamination, while dark, gritty fluid suggests overdue changes.
For precision, use a digital oil level sensor if your vehicle model includes one, accessible via the dashboard menu. Track changes over time in a logbook or app, noting mileage, date, and amount added. This data reveals patterns, helping differentiate normal use from anomalies.
Interpreting Normal vs. Excessive Oil Consumption
Deciphering consumption rates requires context. Ford specifies that up to one quart per 1,200 to 3,000 miles falls within acceptable limits, varying by model year and usage. Calculate your rate by dividing quarts added by miles driven since the last fill-up. For instance, if you add half a quart after 1,500 miles, that's a moderate 3,000 miles per quart.
Excessive use often manifests through symptoms like a persistent oil smell in the cabin or visible leaks under the vehicle. In Coyotes, common culprits include PCV system clogs, which allow oil to enter the intake, or worn piston rings from aggressive driving. Compare your figures against community benchmarks from forums or service bulletins—Gen 1 engines might consume more than Gen 3 variants with improved ring packs.
To refine your assessment, perform a compression test or use an oil catch can to quantify blow-by gases. These insights empower owners to address issues early, maintaining peak performance without overreacting to minor fluctuations.
Common Causes of Elevated Oil Use in Coyote Engines
Delving deeper, several factors contribute to heightened oil consumption in the Coyote V8. Piston ring wear tops the list, especially in high-mileage units where rings fail to seal properly, allowing oil to seep into combustion chambers. Valve guide seals can degrade over time, particularly if exposed to subpar lubricants or infrequent changes.
Other contributors include:
Faulty PCV valves that don't regulate crankcase pressure, leading to oil mist entering the intake manifold.
Turbocharger seals in supercharged variants, though less common in stock Coyotes.
External leaks from gaskets, such as the timing chain cover or oil pan, often exacerbated by vibrations from rough roads.
Improper oil viscosity—using thicker grades than specified can hinder flow, mimicking consumption issues.
Understanding these root causes transforms monitoring from a chore into a diagnostic adventure, where each check uncovers clues about your engine's health.
Effective Maintenance Strategies to Minimize Consumption
Proactive care is key to curbing oil use in your Coyote. Start with adhering to Ford's service intervals, changing oil every 5,000 to 7,500 miles using full synthetic formulations designed for high-heat tolerance. Upgrading to a high-flow oil filter can trap more contaminants, reducing wear on internals.
Incorporate these habits:
Install an oil separator to capture vapors before they re-enter the intake, a popular mod among enthusiasts.
Regularly inspect hoses and seals during tune-ups, replacing any showing cracks or softening.
Opt for break-in procedures on new or rebuilt engines to properly seat rings, minimizing initial consumption.
Monitor coolant levels alongside oil, as overheating can accelerate evaporation.
By integrating these into your routine, you'll not only extend the Coyote's lifespan but also enhance its responsiveness, making every drive more exhilarating.
Advanced Monitoring Techniques for Enthusiasts
For those diving deeper, advanced tools elevate oil monitoring. Invest in an OBD-II scanner to read live data on oil pressure and temperature, spotting deviations in real-time. Laboratory oil analysis kits provide microscopic insights—send samples to reveal metal particles indicating wear or fuel dilution affecting viscosity.
Experiment with aftermarket gauges for dashboard integration, offering at-a-glance visibility during performance runs. Track seasonal variations; winter cold starts might increase consumption due to thicker oil flow. Combining these with driving logs creates a comprehensive profile, allowing predictive maintenance that keeps your Coyote roaring reliably.
More from Ford

Ford F-150: Active Grille Shutter Maintenance and Cleaning Guide
28.12.2025 11:29
Ford Maverick Hybrid: Battery Cooling Fan Cleaning Tips
28.12.2025 08:22
Ford EcoBoost: Preventing Cam Phaser Rattle with Regular Oil Changes
28.12.2025 05:53
Ford F-150: How to Perform Tire Rotation and Balance Every 5,000 Miles
27.12.2025 14:45
Ford F-150 Aluminum Body: Corrosion Protection Tips
25.12.2025 14:18
