Ford Suspension: Greasing Ball Joints and Tie Rods Tips
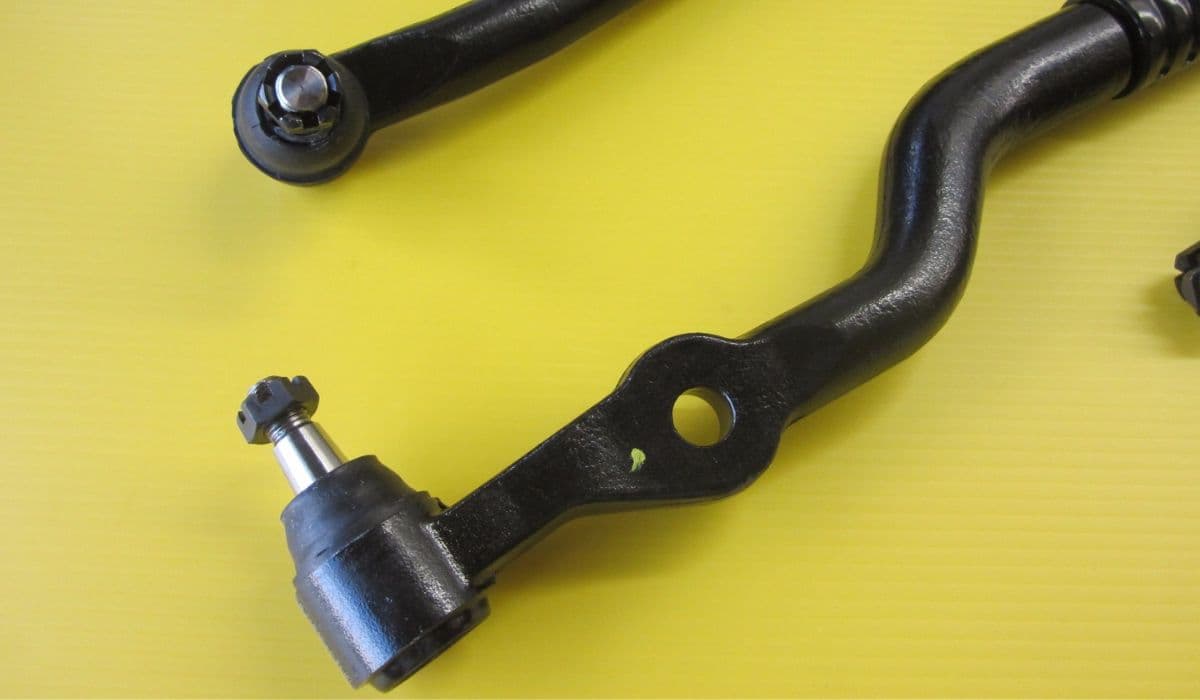

In the intricate world of automotive suspension systems, ball joints and tie rods play pivotal roles, especially in Ford models known for their robust handling and durability. Ball joints act as flexible pivots connecting the control arms to the steering knuckles, allowing smooth wheel movement over bumps and during turns. Tie rods, on the other hand, link the steering rack to the knuckles, translating steering wheel inputs into precise directional changes. For Ford owners, from the rugged F-150 trucks to the agile Mustang coupes, maintaining these components ensures a safer, more responsive drive. Neglecting lubrication can lead to premature wear, manifesting as clunks, vibrations, or uneven tire tread, turning a thrilling road experience into a frustrating ordeal.
What makes greasing these parts so crucial? Over time, dirt, moisture, and road debris infiltrate the joints, eroding the protective grease layer. Regular greasing replenishes this barrier, reducing friction and extending component life. Interestingly, Ford's engineering often incorporates zerk fittings—those small grease nipples—making DIY maintenance accessible even for novice enthusiasts. This process not only preserves performance but also enhances the vehicle's overall suspension geometry, contributing to better alignment and fuel efficiency.
Essential Tools and Materials for Effective Greasing
Before diving into the greasing process, gathering the right tools sets the stage for a seamless operation. A quality grease gun is indispensable, preferably one with a flexible hose for reaching awkward angles in Ford's compact undercarriage layouts. Opt for lithium-based or molybdenum-disulfide grease, as these formulations withstand high pressures and temperatures typical in suspension duties.
Safety gear: Heavy-duty gloves to protect against grease splatters and sharp edges, plus safety glasses to shield eyes from flying debris.
Jack and stands: A hydraulic floor jack paired with sturdy jack stands ensures the vehicle is securely elevated, providing safe access to the suspension.
Cleaning supplies: Wire brushes and degreasers to remove old grime, preventing contamination of fresh grease.
Torque wrench: Essential for re-tightening components to Ford's specified settings, avoiding over- or under-tightening that could compromise safety.
These items transform a potentially messy task into a controlled, efficient procedure, allowing you to focus on the nuances of each Ford model's suspension design.
Step-by-Step Guide to Greasing Ball Joints on Ford Models
Greasing ball joints requires precision to avoid damaging seals or introducing air pockets. Start by parking on a level surface and engaging the parking brake. Lift the front end using the jack, securing it on stands at designated points—consult your Ford owner's manual for exact locations to prevent frame damage.
Locate the ball joints, typically at the upper and lower control arms. Wipe the zerk fittings clean to ensure no contaminants enter. Attach the grease gun coupler firmly, pumping slowly until fresh grease emerges from the boot edges, signaling full lubrication. This extrusion pushes out old, degraded grease, refreshing the joint's internals.
Pump methodically: Apply 2-3 pumps per joint, pausing to check for leaks or swelling in the rubber boots.
Rotate wheels: For comprehensive coverage, turn the steering wheel lock-to-lock while greasing, distributing lubricant evenly.
Wipe excess: Remove any overflow to prevent attracting dirt, which could accelerate wear.
In Ford trucks like the Explorer, ball joints endure heavier loads, so inspect for play or noise beforehand. This hands-on approach not only maintains smoothness but also offers a chance to spot early signs of wear, like cracked boots or loose fittings.
Expert Tips for Greasing Tie Rod Ends
Tie rods demand similar attention but with a focus on their linear motion. These components are exposed to constant twisting forces, making thorough greasing vital for steering precision. Begin by straightening the wheels to relieve tension, then elevate the vehicle as before.
Identify the tie rod ends, often equipped with zerk fittings near the ball-and-socket joints. Clean them meticulously before attaching the grease gun. Pump until resistance builds and clean grease appears, indicating saturation.
Angle considerations: In Ford sedans such as the Fusion, tie rods sit at varying angles; use a swivel coupler on your grease gun for optimal access.
Check for binding: After greasing, manually move the tie rods to ensure free movement, addressing any stiffness immediately.
Dual-end approach: Grease both inner and outer tie rods if applicable, as some Ford designs feature adjustable setups for alignment tweaks.
This maintenance ritual sharpens steering response, reducing wander on highways and enhancing cornering confidence. For off-road enthusiasts with Ford Broncos, frequent greasing counters the abrasive effects of mud and sand.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even seasoned mechanics encounter hurdles when greasing suspension parts. One frequent error is over-greasing, which bursts seals and invites contaminants. To sidestep this, monitor boot expansion closely and stop at the first sign of excess.
Another issue arises from using incompatible greases, leading to chemical reactions that harden the mixture. Stick to manufacturer-recommended types for Ford's specific metallurgy. Ignoring vehicle-specific quirks, like the tighter clearances in compact Fords versus full-size vans, can result in incomplete lubrication.
Temperature awareness: Grease in cold weather; warm conditions thin the lubricant, improving flow but risking drips.
Post-grease test drive: Always road-test afterward to detect unusual noises, confirming successful application.
Documentation: Note the date and mileage in a log, building a maintenance history for future reference.
By anticipating these challenges, you elevate your greasing routine from basic upkeep to proactive vehicle care, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Optimizing Maintenance Schedules for Longevity
Tailoring a greasing regimen to your driving habits maximizes benefits. For daily commuters in urban settings, aim for every 5,000-7,000 miles, aligning with oil changes for convenience. Off-road or heavy-duty use in Ford vehicles demands more frequent intervals, perhaps every 3,000 miles, to combat accelerated wear.
Seasonal factors influence timing too—grease before winter to protect against salt corrosion, or after summer adventures to flush out heat-induced degradation. Integrating this with tire rotations creates a holistic suspension care strategy.
Monitor symptoms: Unusual steering pull or suspension squeaks signal the need for immediate attention.
Model variations: Consult Ford forums or service bulletins for nuances in models like the Ranger, where suspension loads differ.
Professional touch: If unsure, a quick mechanic inspection complements DIY efforts, blending expertise with hands-on involvement.
This proactive stance transforms routine maintenance into an engaging aspect of ownership, fostering a deeper connection with your Ford's engineering prowess.
More from Ford

Ford F-150: Active Grille Shutter Maintenance and Cleaning Guide
28.12.2025 11:29
Ford Maverick Hybrid: Battery Cooling Fan Cleaning Tips
28.12.2025 08:22
Ford EcoBoost: Preventing Cam Phaser Rattle with Regular Oil Changes
28.12.2025 05:53
Ford F-150 Aluminum Body: Corrosion Protection Tips
25.12.2025 14:18
Parasitic Battery Drain Diagnosis and Fix Ford F-150
24.12.2025 06:08
