GR Corolla G16E-GTS Engine Tuning Potential
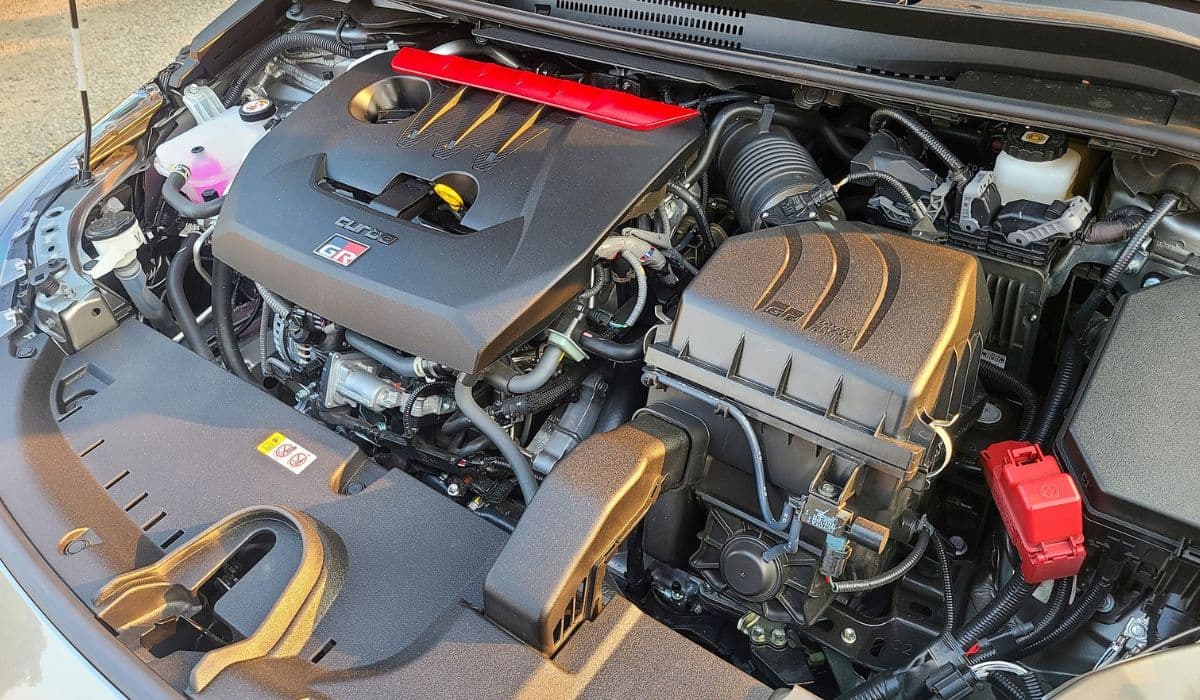

The Toyota GR Corolla arrived with one of the most exciting factory turbocharged three-cylinders ever put in a production car – the G16E-GTS. This 1.6-liter inline-three produces 300 hp (304 PS) and 273 lb-ft (370 Nm) in stock form, making it the most powerful production three-cylinder engine in history. What makes it truly special for enthusiasts is not just the headline numbers, but the enormous tuning headroom built into virtually every component.
Engine Block and Rotating Assembly Strength
The G16E-GTS uses a closed-deck aluminum block with reinforced main bearing girdle and cast-iron cylinder liners. Toyota engineered the block with motorsport in mind, borrowing technology directly from its WRC program. The crankshaft is forged steel with enlarged 52 mm main journals and 48 mm rod journals – dimensions usually seen in much larger displacement engines.
Connecting rods are forged steel with cracked caps and measure 129.9 mm center-to-center. Pistons are cast aluminum with full floating pins and feature oil squirters for cooling. Factory compression ratio sits at 9.2:1 (some markets 9.5:1), leaving significant room for boost increases without immediate detonation issues when proper fuel and tuning are applied.
Real-world testing has shown the stock bottom end reliably handling over 500 wheel horsepower on pump gas and race fuel combinations, with documented builds exceeding 600 whp while remaining daily-drivable.
Cylinder Head and Valvetrain
The 4-valve-per-cylinder head is a masterpiece of compact engineering. It features laser-cladded valve seats – the same technology used in Toyota’s NASCAR and Le Mans engines – providing exceptional durability under extreme heat and boost. Ports are CNC-optimized with excellent flow characteristics that respond dramatically to mild porting.
Variable valve timing (VVT-i) is present on both intake and exhaust camshafts, allowing tuners to optimize cam timing across the entire powerband. Factory valve springs are surprisingly robust and rarely require upgrading until well past 550 whp.
Turbocharger and Boost System
Stock turbo is a single-scroll Mitsubishi TD04HL with integrated exhaust manifold. While small in appearance, it features a lightweight titanium-aluminum turbine wheel and responds instantly with virtually zero perceptible lag. Factory boost peaks at approximately 25–26 psi and tapers to 20–22 psi in the mid-range.
The real magic happens when replacing the stock unit. The integrated manifold design actually helps rather than hinders big-turbo conversions, as companies now offer bolt-on hybrid and larger frame turbo kits that retain the factory manifold while flowing dramatically more air.
Popular upgrades include:
Hybrid TD04 variants with larger compressor wheels making 380–450 whp
Garrett G25-550 and G30-660 bolt-on kits pushing 500–600+ whp
Precision and Xona Rotor options for 700+ whp builds
Fuel System Capacity
Direct injection operates at up to 290 bar (4200 psi) through multi-hole injectors with excellent atomization. The factory high-pressure pump flows considerably more than needed for stock power levels. Most tuners report the stock HPFP supporting 480–520 whp on E85 before requiring upgrade.
Port injection supplementation has become extremely popular, with companies offering complete bolt-on kits that add 1000–1500 cc/min of additional fuel capacity. These kits typically enable 650–800+ whp capability when combined with larger turbos and E85 or methanol blends.
Cooling System and Thermal Management
Toyota massively over-engineered cooling for sustained track use. The GR Corolla features triple radiators (central main radiator plus two side-mounted units), dedicated transmission and differential coolers, and an engine oil cooler. Many owners report coolant temperatures staying below 220°F even during extended track sessions.
Intercooler is a large front-mount unit with excellent flow characteristics. Core dimensions support over 600 whp before significant heat soak becomes an issue. Upgraded drop-in replacements and larger front-mount options are readily available for extreme builds.
Engine Management and Tuning Options
The factory ECU proved remarkably flexible. Multiple companies now offer true plug-and-play tuning solutions:
EcuTek with full custom mapping capability and advanced features (launch control, flat-foot shifting, flex-fuel, etc.)
Cobb Accessport with extensive off-the-shelf maps
Standalone options (Haltech, AEM Infinity, MoTeC) for extreme builds
The engine responds exceptionally well to tuning, with many owners gaining 80–100 whp from simple Stage 1 ECU flashes on 93 octane while maintaining perfect drivability.
Transmission and Drivetrain Considerations
While not strictly engine-related, the GR-Four AWD system and 6-speed manual transmission play crucial roles in power delivery. The stock clutch begins slipping around 350–380 lb-ft of torque, making it the first typical upgrade point. Reinforced clutch options and the factory automatic GR Corolla clutch (higher capacity) have become popular solutions.
Front and rear differentials use Torsen limited-slip units with electronic clutch packs for torque vectoring. These have proven durable to approximately 550–600 whp before requiring upgraded clutch packs or complete aftermarket differentials.
Proven Power Levels and Reliability
Real-world examples show the G16E-GTS achieving remarkable power levels with surprising reliability:
400–450 whp: Completely safe on stock engine internals with basic bolt-ons
500–550 whp: Stock bottom end limit for most builders seeking long-term reliability
600–650 whp: Possible with careful assembly, upgraded rods, and meticulous tuning
700–900+ whp: Achieved with fully built engines, sleeved blocks, forged internals
Many 500+ whp cars are driven daily and tracked regularly with no engine failures when properly maintained.
Exhaust and Intake Modifications
The factory exhaust features a unique triple-outlet design with active valve system. Cat-back exhausts typically gain 15–25 whp while dramatically improving sound. Downpipe upgrades (catted or catless) add another 30–50 whp when combined with proper tuning.
Intake modifications show modest gains (10–20 whp) due to the excellent factory cold-air system, but aftermarket options improve turbo spool characteristics and sound dramatically.
Oil System and Lubrication
Factory oil pump is gear-driven and high-volume. Oil starvation has not been reported as an issue even during aggressive track driving. Many high-power builders upgrade to improved oil coolers and baffles for additional safety margin.
The G16E-GTS represents a golden era of tunable performance engines – combining bulletproof construction, massive factory safety margins, and exceptional aftermarket support. Few engines in history have offered this combination of compact size, instant response, and 600+ horsepower potential while maintaining daily drivability and reasonable longevity when properly modified.
More from Toyota

2024+ Toyota Land Cruiser 2.4T Hybrid Real-World MPG: What Owners Actually Get
08.12.2025 13:31
RAV4 Prime vs Hybrid Battery Differences: A Deep Technical Comparison
08.12.2025 13:28
8-Speed vs 10-Speed Transmission Toyota Reliability: In-Depth Real-World Comparison
08.12.2025 13:15
Common 3rd Generation Toyota Tundra 3.4L Twin-Turbo V6 (V35A-FTS) Engine Problems 2022–2025 Models
08.12.2025 13:18
2UZ-FE 4.7 V8 vs 3UR-FE 5.7 V8 Reliability: In-Depth Real-World Comparison
08.12.2025 13:24
