How to fix drivetrain malfunction error BMW (2025 models)

The drivetrain malfunction warning on modern BMW models can appear suddenly, often accompanied by reduced power, a check engine light, or even a "do not drive" message. This alert serves as a protective mechanism, signaling that the engine, transmission, or related systems have detected an irregularity that could affect performance or safety. In newer models, the warning frequently stems from sophisticated electronic monitoring rather than outright mechanical failure, but ignoring it risks entering limp mode or secondary damage.
Understanding the root causes and following a structured troubleshooting approach helps owners address the issue efficiently. Many cases resolve through simple resets or minor fixes, while others require precise diagnostics.
Understanding the Drivetrain Malfunction Warning
BMW's drivetrain malfunction message is intentionally broad. It covers the entire power delivery chain—from engine combustion to transmission output and even electric components in hybrid or electric variants. The system monitors parameters like torque delivery, sensor readings, and actuator responses in real time.
When values deviate from expected ranges, the digital dashboard displays the warning. Common accompanying symptoms include:
Sudden loss of acceleration or power
Rough idling or vibrations
Transmission hesitating during shifts
Vehicle entering reduced-power limp mode
Check engine light illumination
In many instances, the message clears after a restart, but recurring appearances indicate an underlying fault that needs attention.
Initial Safety Steps When the Warning Appears
Safety comes first when this alert activates. Pull over safely if driving aggressively or at high speeds, as power reduction can compromise control.
Turn off the engine and wait 5–10 minutes before restarting. This allows modules to reset and often clears transient glitches.
Avoid heavy acceleration or high-load driving until the issue is resolved.
If the message includes "do not drive" or severe power loss, arrange for towing rather than risking further travel.
A quick reboot using the infotainment hard reset—holding the volume button for 30–60 seconds—has resolved intermittent warnings for some owners by forcing a full system refresh.
Performing a Basic Reset at Home
Many drivetrain malfunctions, especially software-related or voltage-induced ones, disappear after a proper reset. Try these steps in order:
Simple engine restart: Shut off the vehicle completely, remove the key (or wait for full shutdown in push-button models), wait several minutes, then restart.
Battery disconnect method: Disconnect the negative battery terminal for 15–20 minutes. This discharges residual power in control modules and can clear temporary faults. Reconnect securely and start the engine.
Infotainment reboot: Press and hold the volume knob for up to 60 seconds until the screen restarts. This refreshes electronic systems without affecting stored settings.
If the warning returns immediately or intermittently, proceed to diagnostics—the reset only masks symptoms in persistent cases.
Scanning for Fault Codes: The Essential Next Step
Modern BMWs store detailed fault codes in multiple modules (DME for engine, EGS for transmission, and others). Generic OBD-II scanners often miss BMW-specific codes, so use a tool compatible with enhanced diagnostics.
Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port under the dashboard.
Read codes from powertrain-related modules.
Note common codes like misfire counts (P0300 series), fuel pressure faults, or communication errors.
Popular free resources or BMW-specific code interpreters help translate these into actionable insights. Clearing codes without fixing the root cause usually results in their return, often with the same symptoms.
Common Causes and Targeted Fixes
Several recurring issues trigger this warning in recent BMWs. Addressing them systematically improves success rates.
Weak or failing 12V battery: Low voltage disrupts module communication and sensor accuracy. Many intermittent cases trace back to an aging battery struggling under load.
Engine misfires: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or injectors cause irregular combustion, triggering the alert during acceleration.
Fuel delivery problems: Clogged injectors, failing high-pressure fuel pumps, or poor fuel quality lead to inconsistent pressure and power delivery.
Sensor and electrical faults: Camshaft/crankshaft position sensors, turbo boost sensors, or wiring harness issues send erratic signals.
Transmission-related glitches: Fluid condition, solenoid problems, or software mismatches in the ZF automatic units appear as drivetrain faults.
Software bugs: Over-the-air updates or module calibration errors cause false positives, especially in newer models with complex hybrid systems.
For electric or plug-in hybrid variants, check high-voltage battery health or charging unit faults, as voltage irregularities often mimic drivetrain issues.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
When basic steps fail, deepen the investigation:
Inspect fluid levels (engine oil, transmission fluid) for proper quantity and condition—low or contaminated fluids exacerbate problems.
Monitor live data during a test drive: Watch fuel trims, misfire counters, and boost pressure for anomalies.
Check for aftermarket modifications: Tuned software or hardware changes sometimes conflict with factory safeguards.
Examine auxiliary components: In some cases, issues like EGR valve sticking or catalytic converter restrictions indirectly trigger the warning.
Document when the fault occurs—cold starts, hot conditions, highway cruising—to narrow possibilities.
When Professional Help Becomes Necessary
Persistent or severe warnings warrant expert intervention. Dealerships or specialized independents access proprietary software for deeper module analysis, software updates, and adaptations.
Recurring software-related faults often receive free updates, while hardware issues like sensor replacement or harness repairs restore full function. Early diagnosis prevents cascading failures, such as unaddressed misfires damaging catalytic converters.
Preventing Future Drivetrain Malfunction Warnings
Proactive maintenance reduces recurrence:
Follow BMW's service intervals rigorously, especially for spark plugs, filters, and fluids.
Use high-quality fuel from reputable stations to avoid injector or pump issues.
Monitor battery health annually, as voltage stability is critical in modern electronics-heavy vehicles.
Keep software updated through official channels.
Address small performance changes promptly rather than waiting for warnings.
By staying attentive to these details, owners maintain optimal drivetrain reliability and enjoy the dynamic performance BMWs are known for.
More from BMW
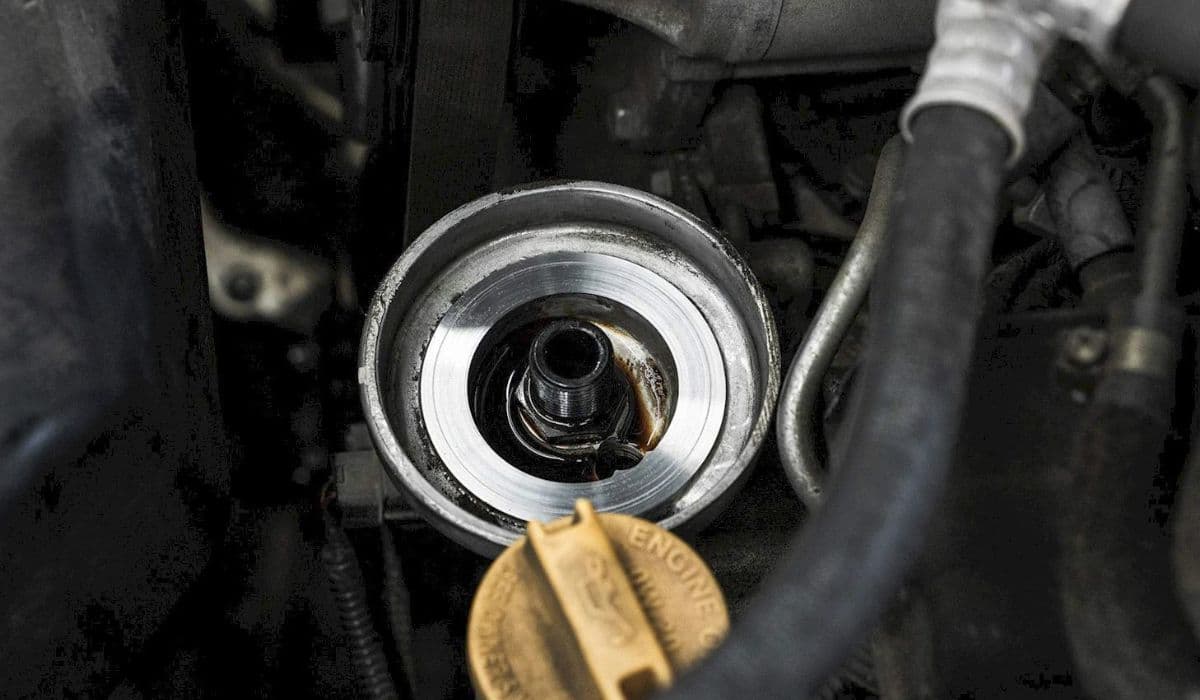

How to fix oil filter housing gasket (OFHG) leak BMW
13.12.2025 06:13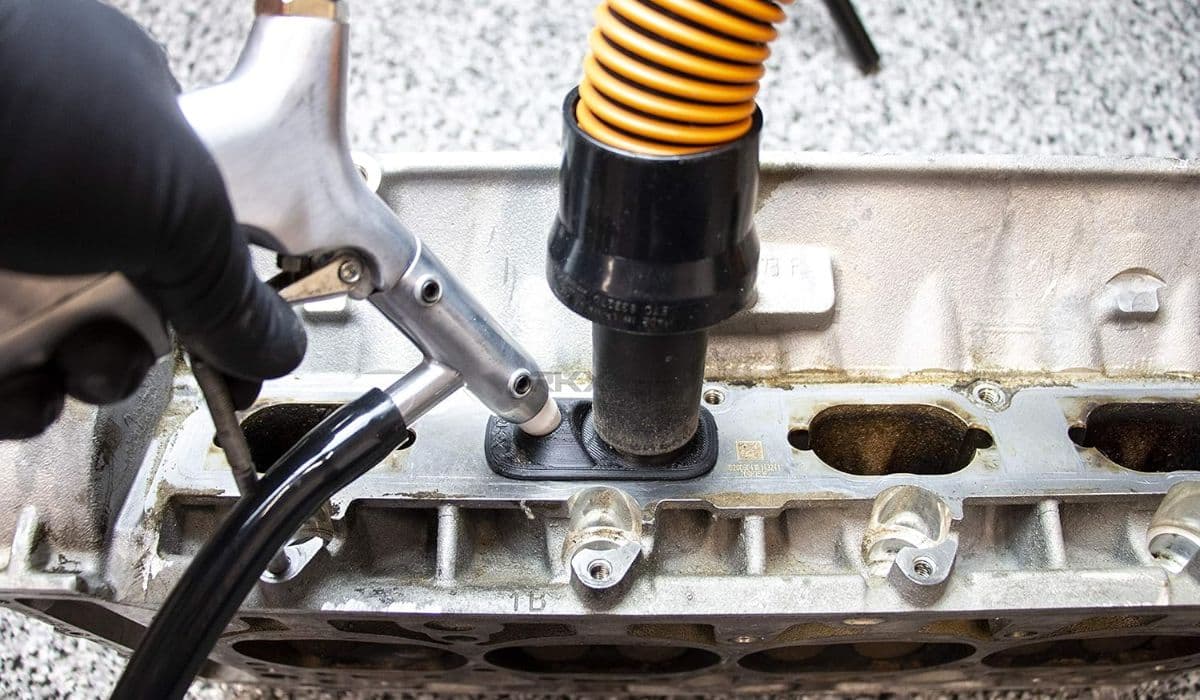
How to walnut blast intake valves for carbon buildup BMW
13.12.2025 06:07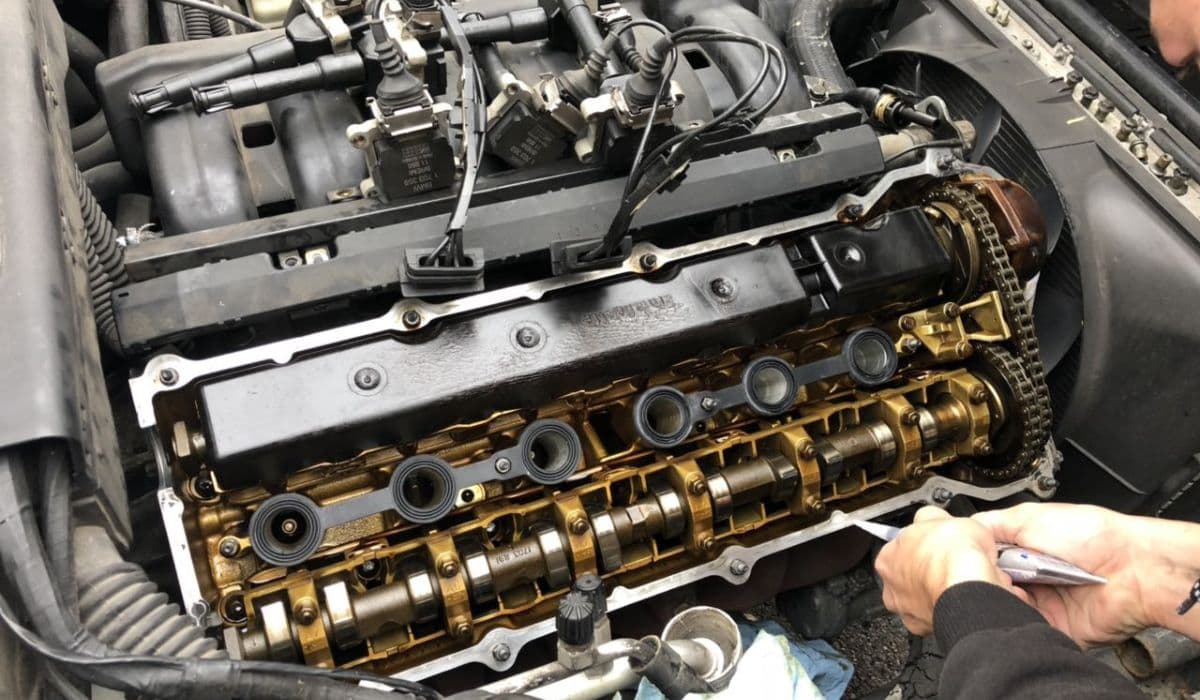
How to replace valve cover gasket oil leak BMW (common on N20/N55)
13.12.2025 05:40
How to fix VANOS solenoid rattle and codes BMW
13.12.2025 05:32
How to replace timing chain guides BMW (N20/N55 preventive)
13.12.2025 03:18
