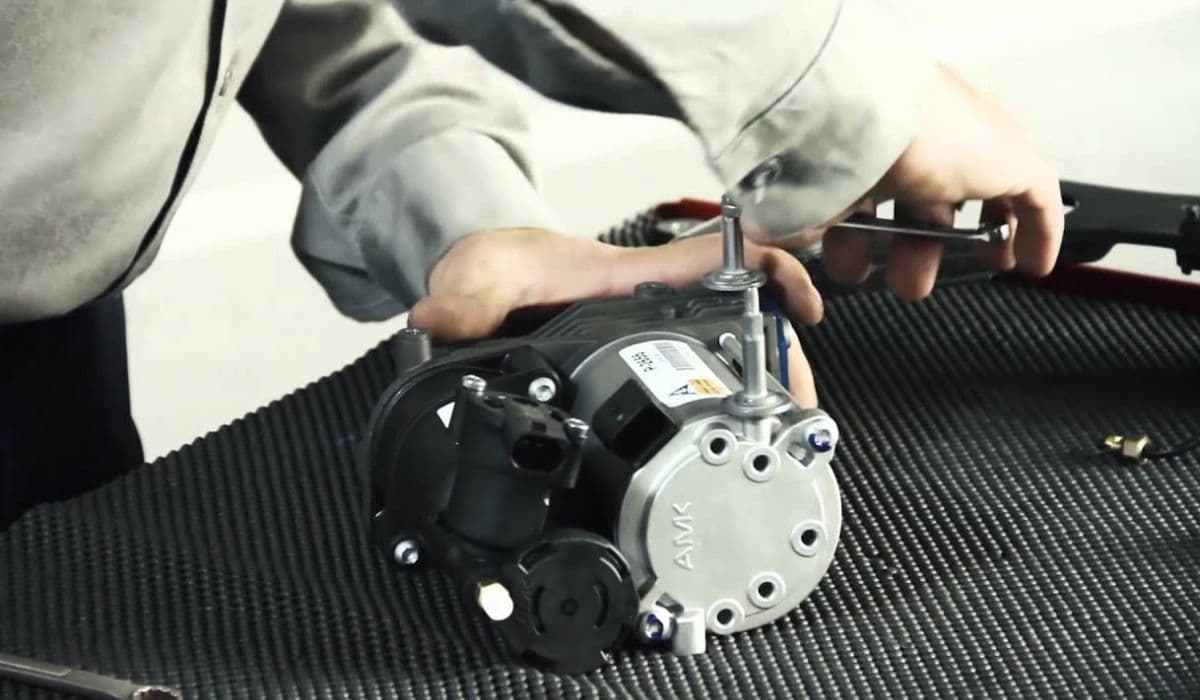
How to fix electronic parking brake malfunction BMW
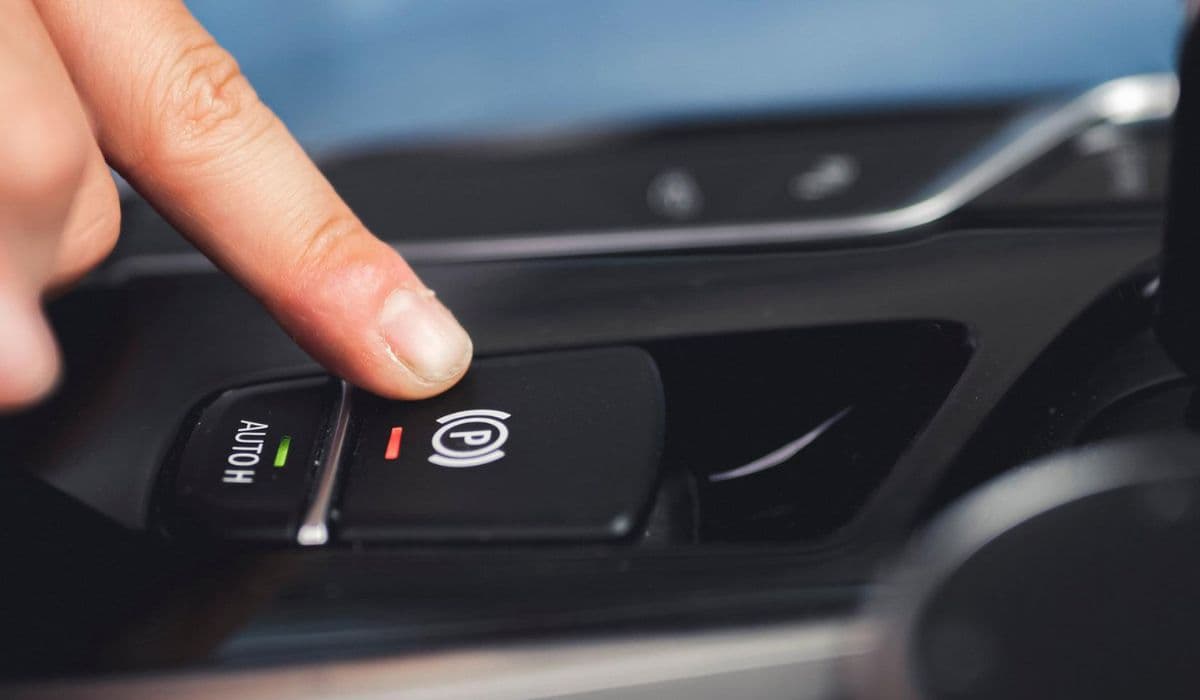

BMW's electronic parking brake (EPB) system represents a significant advancement over traditional mechanical handbrakes, offering seamless integration with features like auto-hold and hill start assist. However, when a malfunction occurs, it can trigger warning lights, limit functionality, and leave drivers concerned about safety. Understanding the root causes and systematic troubleshooting steps can help restore proper operation efficiently.
Understanding the BMW Electronic Parking Brake System
The EPB in modern BMW models replaces cable-operated mechanisms with electric actuators that clamp the rear brake calipers. A central control module communicates with sensors, motors, and the vehicle's stability systems to engage or release the brake automatically or via a dashboard switch.
This setup provides precise control and convenience, such as dynamic braking during emergencies or automatic engagement when the engine is off. Yet, its reliance on electronics makes it susceptible to issues that mechanical systems rarely face, turning a simple parking feature into a complex diagnostic challenge.
Common Symptoms of EPB Malfunction
Recognizing early signs allows for timely intervention before the system fails completely. Typical indicators include:
A persistent yellow "PARK" or brake warning light on the dashboard, even when driving.
Messages like "Parking Brake Malfunction" or "Limited Function" appearing on the iDrive screen.
Inability to engage or release the parking brake using the switch.
Unusual noises, such as grinding or whirring, from the rear wheels during operation.
Auto-hold feature becoming unavailable or erratic behavior in related systems like dynamic stability control.
These symptoms often stem from intermittent faults that worsen over time, affecting multiple driver assistance functions.
Primary Causes of Electronic Parking Brake Issues
Several factors contribute to EPB failures in BMW vehicles, ranging from simple electrical glitches to mechanical wear.
The most frequent culprit is the parking brake actuator, a motor-driven unit that can suffer internal gear damage or motor seizure due to moisture ingress or prolonged inactivity. Low battery voltage is another common trigger—BMW's sensitive electronics detect even minor drops, falsely interpreting them as system faults.
Other causes include:
Faulty wheel speed sensors or disrupted wiring harnesses sending incorrect data to the control module.
Corroded connectors or blown fuses in the EPB circuit.
Software glitches in the control unit requiring updates.
Worn brake components interfering with actuator movement.
Environmental factors, like water exposure in the trunk area where wiring runs, can accelerate these problems.
Initial Troubleshooting Steps
Before escalating to advanced repairs, perform these non-invasive checks to resolve many malfunctions.
Start with the battery: Ensure it holds sufficient charge, as weak voltage often mimics serious faults. Clean terminals and test for stable output.
Inspect visible wiring around the rear calipers and trunk for damage or loose connections. Check relevant fuses in the glovebox or luggage compartment panels.
A simple reset can clear temporary errors:
Turn the ignition on (engine off).
Firmly depress the brake pedal.
Press and hold the parking brake switch for several seconds to cycle the actuators.
Listen for normal operation sounds.
For some models, entering service mode via the instrument cluster allows manual recalibration of rear brakes.
Diagnostic Procedures
Accurate diagnosis requires reading fault codes from the EPB module, which standard OBD scanners cannot access fully.
Use a BMW-compatible diagnostic tool to scan the electromechanical parking brake (EMF) and related modules like ABS/DSC. Common codes point to actuator faults, sensor issues, or communication errors.
Observe the system in action: Engage and release the brake multiple times while monitoring for consistent motor response. Acoustic feedback from the rear indicates healthy actuators.
If codes persist after clearing, trace them systematically—starting with power supply, then sensors, and finally mechanical components.
Resetting the EPB System
Many malfunctions resolve with a proper reset, especially after battery disconnection or minor glitches.
One effective method involves:
Ignition on, engine off.
Hold the brake pedal down firmly.
Pull the parking brake switch to engage, wait, then push to release—repeat several cycles.
Alternatively, hold the switch in the release position while monitoring for beeps or light changes.
For integrated systems in newer chassis, access hidden menus through button combinations on the start/stop and cluster controls to initiate recalibration.
After resets, test thoroughly: Park on an incline to verify holding power and ensure no warnings return during drives.
Advanced Repairs and Actuator Issues
When resets fail, the actuator often needs attention. Internal plastic gears can strip, causing mechanical failure despite electrical signals.
Disassemble the unit carefully to inspect for broken components. Some owners replace worn gears with more durable alternatives for a long-term fix.
In cases of seized motors from rust, cleaning and lubrication may revive them, though replacement is safer for reliability.
Wiring repairs involve splicing damaged sections or replacing harness segments prone to chafing.
Always recalibrate the system post-repair using diagnostics to adapt to new components.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Proactive care extends EPB lifespan significantly.
Regularly cycle the parking brake, even in automatic transmission vehicles, to prevent seizure from disuse.
Keep the battery in top condition and avoid deep discharges.
Inspect rear brakes during routine service for early wear signs.
Protect wiring from moisture, especially in regions with harsh weather.
Stay current with software updates during dealer visits.
These habits minimize unexpected failures and maintain the system's integration with other safety features.
Addressing an electronic parking brake malfunction in a BMW demands patience and methodical steps, but most issues yield to targeted troubleshooting. By starting with basics like battery health and resets, progressing to diagnostics, and tackling hardware when necessary, owners can often restore full functionality without extensive downtime.
More from BMW

How to fix starter-generator loose connection BMW
19.12.2025 16:00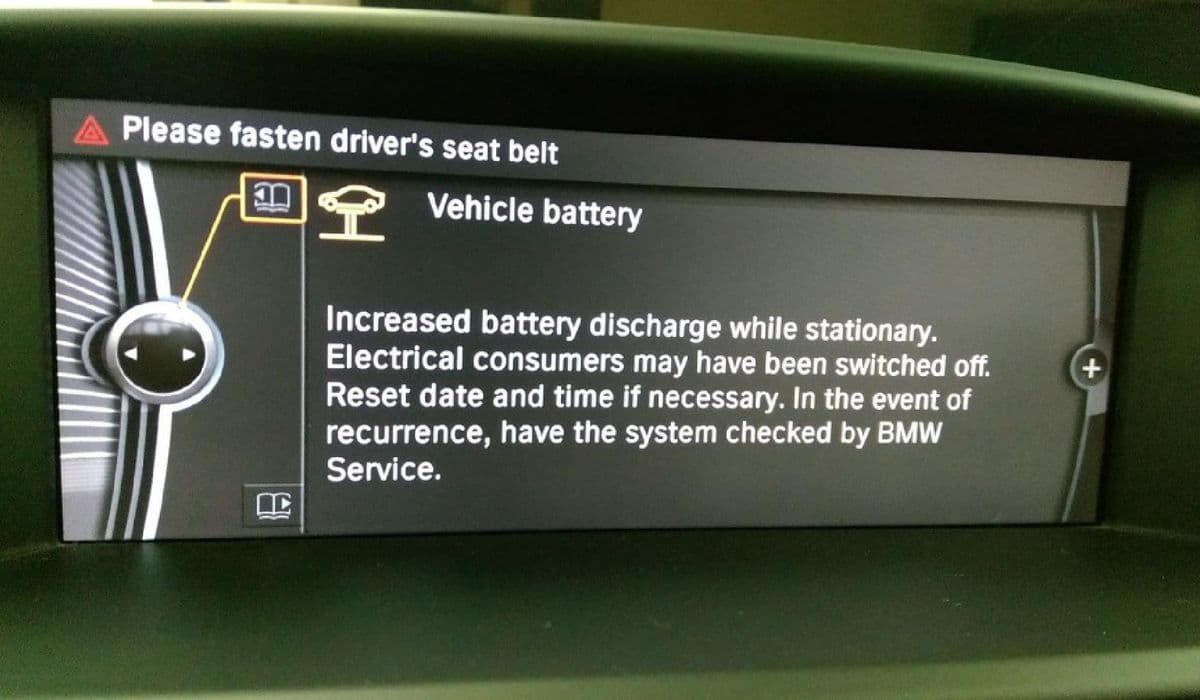
How to fix high-voltage battery shutdown (BMW i4/iX recall)
14.12.2025 14:38
How to replace starter-generator connection BMW
14.12.2025 11:51
How to fix panoramic roof noise or leaks BMW
14.12.2025 07:56
How to fix brake booster vacuum issues BMW
14.12.2025 06:06
